Calf Muscle Physiology
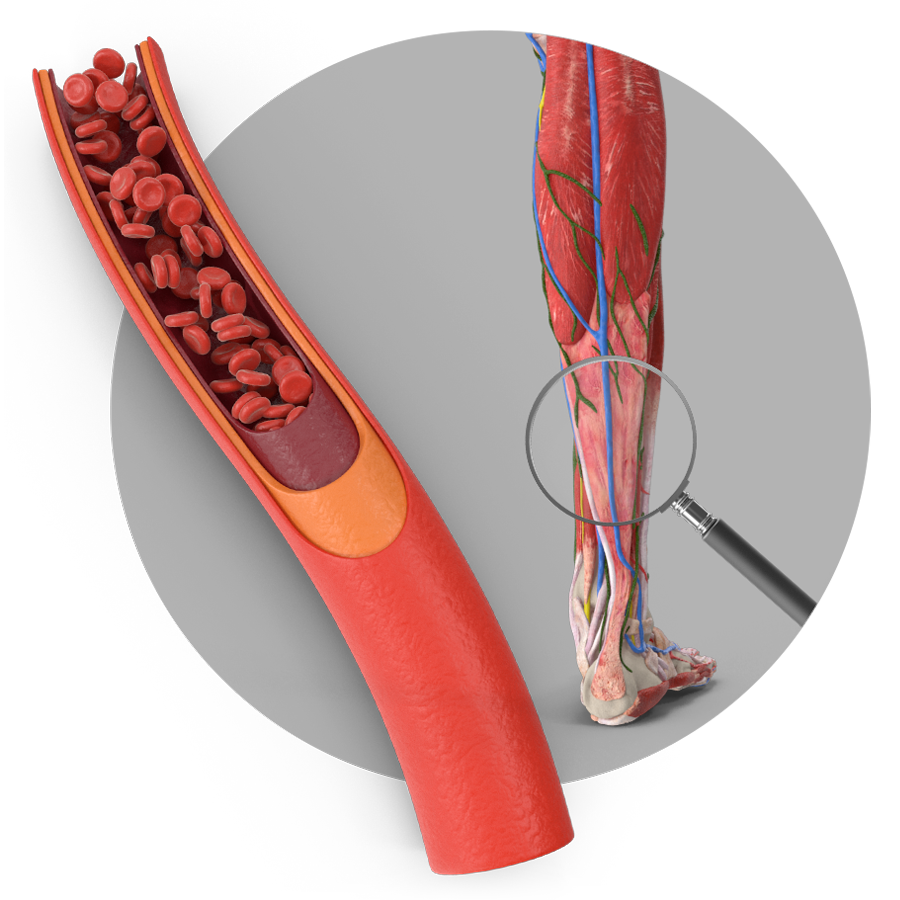
Deep vein plexus in calf muscle
Understanding The Physiology
Any factor that disrupts normal blood flow can lead to the formation of a blood clot
The muscle pump in the calves ensures that the venous return back to the heart works properly. Every time the muscles contract, they squeeze the deep veins in the legs together and transport the blood further.
- The muscle pump only springs into action when we use our muscles, eg. walking or running
- Long periods of standing or sitting can lead to blood pooling in the legs
- Water from the blood can leak through vessel walls into the surrounding tissues and can lead to swollen legs and feet
- Whenever the muscles of the feet and legs are working, the muscle pump works too and jump-starts venous return.
CLOTBuster® In-Flight Passenger Foot Pump is directed at the physiology underlying clot formation by exercising the calf muscles which in turn pumps blood from the deep veins of the calf, to the veins in the thigh, pelvis and back to the heart.
